Protective relays represent a sophisticated aspect of electrical engineering and contracting, often perceived as daunting, but they don’t have to be! This series of three articles aims to introduce the basics of relaying to professionals in the solar and energy storage industries who may not have an engineering background.
---
**Intro to Relays #1 – What Are Relays, CTs, & PTs? (Below on this Page)**
**Intro to Relays #2 – ANSI/IEEE Relay Device Numbers**
**Intro to Relays #3 – What Does SEL Stand For?**
---
### **What Is a Relay?**
The term "relay" can refer to various concepts within the electrical and electronics domains, but in the solar industry, we're specifically talking about "protective relays."
A protective relay monitors a circuit's voltage, current, or frequency. Upon detecting an abnormal condition, the relay triggers a switch to either open or close, thereby isolating the system to prevent damage.
In earlier times, relays were electromechanical devices. Today, however, modern relays are microprocessor-based—essentially computers housed in a compact box.

---
### **Functionality**
The primary purpose of a relay is to swiftly disconnect any equipment that could sustain damage or disrupt the overall system. Protective relays serve two critical functions:
1. **Preventing System Failure:** They ensure that electrical systems remain intact under normal conditions.
2. **Mitigating Damage:** If something does go wrong, relays minimize the impact by isolating problematic areas.
A relay constantly monitors current, voltage, and frequency within a circuit, looking for deviations from standard parameters. Once a monitored value exceeds its designated range, the relay sends a signal to a connected device (like a switch) to open or close before the entire system is compromised.
The "electrical system" safeguarded by relays could be:
- Your solar PV or energy storage system.
- A building or facility.
- The utility's broader power grid.
For instance, an overcurrent relay measures the current on a feeder line. If the current surpasses a preset threshold, it signals a circuit breaker to trip, halting the flow of electricity.
Another example is the reverse power relay, which safeguards the utility grid. If backfeeding current exceeds the utility's limits, it shuts down the solar system to avoid damaging utility equipment.
An overvoltage relay plays a vital role in protecting large-scale solar PV systems' inverters and transformers. When it senses a voltage spike, it isolates the system from potential harm caused by excessive grid voltages.
---
### **Attention Engineers!**
If you're passionate about technical topics like these, Pure Power might be the perfect fit for you! Our team of 80 engineers designs over 2,000 commercial and utility-scale solar projects annually. Surrounding yourself with such expertise can significantly boost your career trajectory.
Explore our open positions [here](#).
---
### **How Do Relays Differ from Circuit Breakers or Fused Switches?**
While circuit breakers and fused switches also interrupt circuits during high current situations, their functionality is largely confined to that. They are limited to being overcurrent devices with minimal adjustability.
On the other hand, relays offer far greater capabilities:
- **Multi-functionality:** Relays can monitor current, voltage, frequency, power factor, and more. Utilities frequently monitor grid voltage and frequency, requiring solar systems to disconnect if production falls outside specified ranges.
- **Custom Programming & Flexibility:** Modern relays are programmed by engineers to operate precisely as required. While multiple projects might use the same relay model, each one can be uniquely configured.
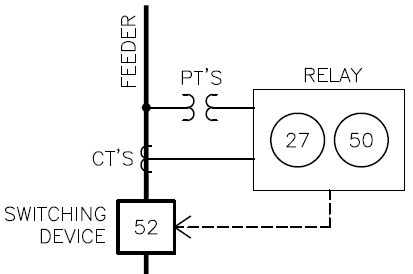
- **Discrete Components:** Unlike circuit breakers, which combine sensing units and switches into one unit, relays consist of separate components—relays themselves, switches, current transformers (CTs), and potential transformers (PTs). Relays can share enclosures but aren't integrated like circuit breakers.
---
### **Understanding CTs and PTs**
#### **CTs (Current Transformers):**
CTs measure current in a circuit. Since most circuits operate at high amperage levels, CTs reduce this current to safer levels for connection to relays. For example, an 800:5 CT ratio steps down a circuit operating between 0–800 amps to a manageable 0–5 amps.

#### **PTs (Potential Transformers):**
PTs measure voltage and frequency in circuits. Similar to CTs, PTs step down excessively high voltages to levels suitable for relays.

---
### **Switching Devices**
Switching devices control the opening (turning off) or closing (turning on) of circuits. Disconnecting a circuit due to abnormal conditions is often called "tripping."
In utility-scale systems, switching devices typically include reclosers or vacuum circuit breakers operating at medium or high voltages. In commercial settings, 480V or 208V circuit breakers or disconnect switches with shunt trip options are common.
---
### **Conclusion**
At first glance, the concept of relaying seems straightforward. Yet, as you delve deeper, its complexity grows rapidly. Developers and project managers don’t need to master every detail to succeed—they rely on seasoned engineers like those at Pure Power. If you require assistance with relays on your project, [click here](#) to learn more or contact us directly today.
---
As technology advances, understanding protective relays becomes increasingly important for anyone involved in renewable energy. Stay tuned for more insights in future articles!
4.5L-8L Air Fryer
KGS customized Air fryers use hot air circulation to cook food that would otherwise be soaked in oil. The cooking chamber of an Air Fryer radiates heat from heating elements near the food for more efficient cooking. A fan is usually used to circulate hot air around the food. The opening at the top is used to draw in air, while the exhaust at the back controls the temperature by releasing any unwanted hot air. It is also used to offset any increase in internal pressure. Internal temperature may be as high as 230°C (445°F) depending on model. For your safety, do not put oil in the fryer or place flammable items near the fryer. Typically, cooking time in an air fryer is reduced by 20% compared to a conventional oven. This will vary by brand and the amount of food cooked in the air fryer.
Large-capacity air fryer can cook more styles of dishes. 4.5L-8L is right for 4-6 people.
4.5L-8L Air Fryer,Air Deep Fryer,Digital Air Fryer,Digital Air Deep Fryer
Guangxi Nanning King Green Smart Co., Ltd. , https://www.smartliferobot.com